Exploring the Functionality and Applications of Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Traditional Website Setup
In traditional website setups, website content is hosted on a single server.
When a user clicks on a URL in their browser, it connects to DNS, which translates the URL into the website's IP address.
The browser then connects directly to that server to retrieve website content.
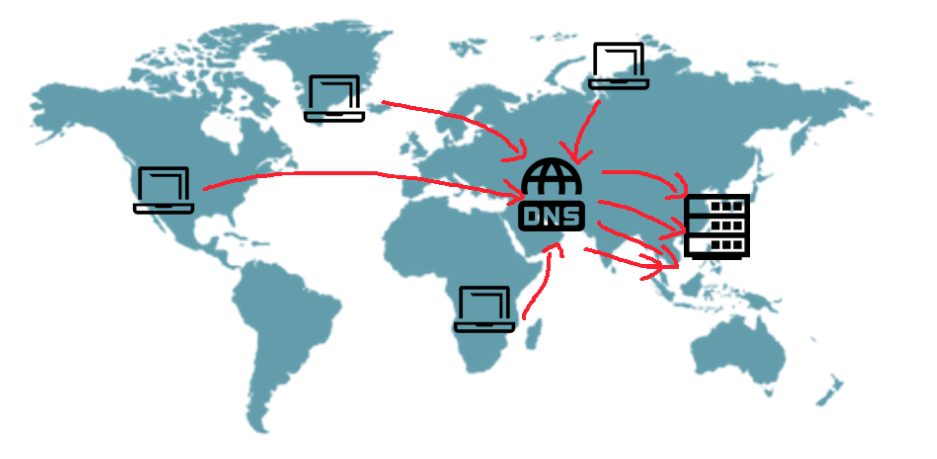
This method has the following disadvantages:
- The farther away a user is from the server, the slower the speed (especially for global websites).
- Server stability is reduced (high traffic and multiple simultaneous connections to the same server increase the chance of a server crash).
Introduction to CDN
This led to the development of CDN.
CDN stands for Content Delivery Network.
It allows website content to be deployed to edge nodes at various locations.
Users from different regions can access the nearest server to retrieve content, providing several advantages:
- Faster load times (reducing physical distance).
- Reduced load on the main server (users access the nearest CDN server, decreasing the load on the origin server).
- Improved reliability (multiple CDN servers reduce the risk of downtime).
- Enhanced user experience (faster connection speeds, quicker website browsing, and reduced risk of site crashes).
CDN Process Diagram:
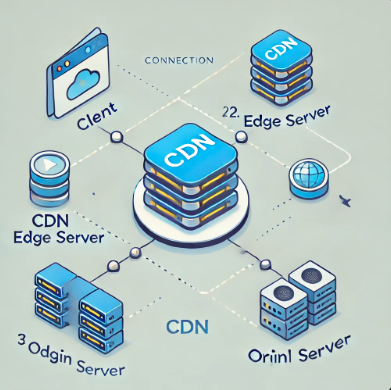
Website content is stored on the primary server.
After configuring CDN, when users connect to the website, they first connect to DNS.
DNS then redirects to CDN DNS.
CDN DNS identifies the user’s location and returns the IP of the closest CDN edge server.
The user connects to the nearest CDN edge server to retrieve website content.
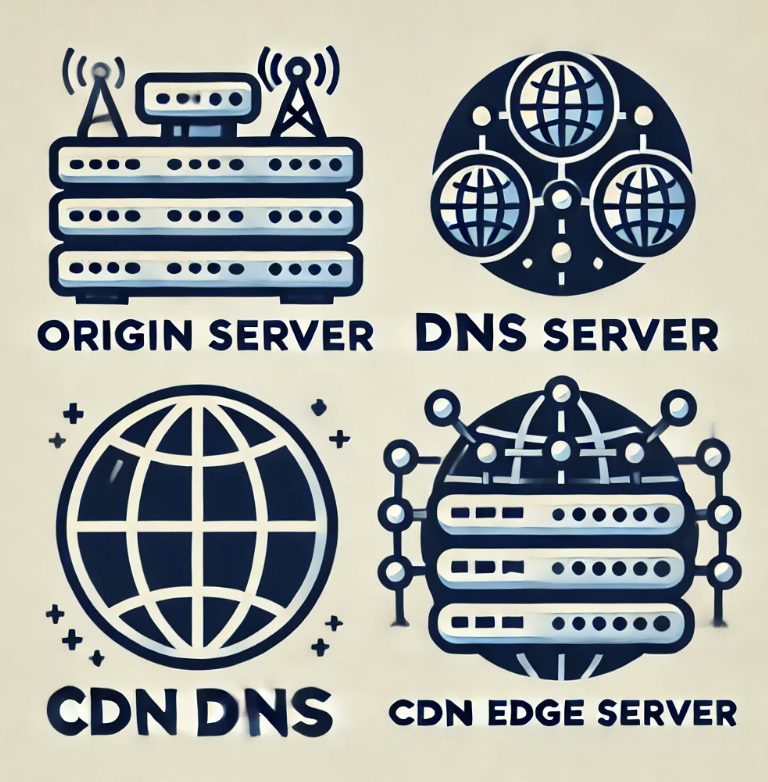
CDN is composed of the following:
- Primary content server (Origin Server)
- DNS
- CDN DNS
- CDN edge servers (CDN servers distributed across different regions)
Practical Demonstration
I uploaded several large GIF files to a test website and placed them far from Taiwan.
Then I tested the load speed for the first time.

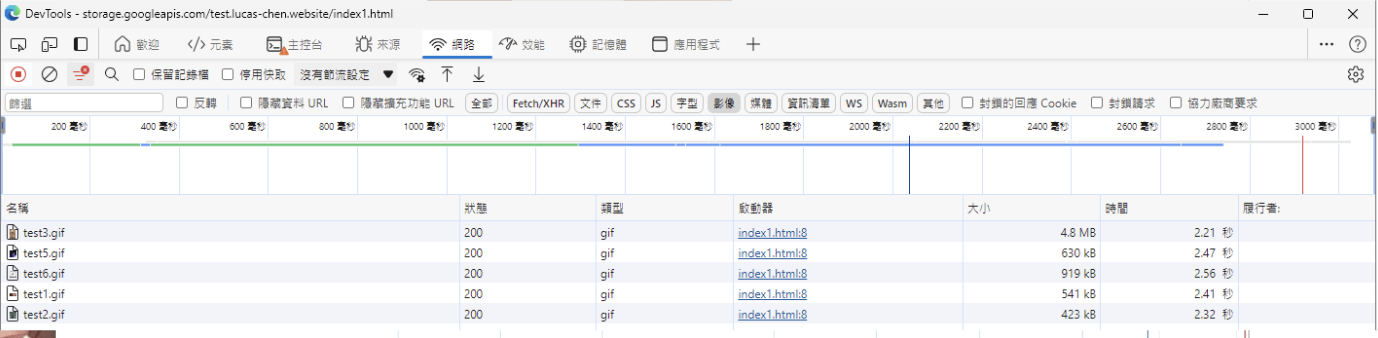
It took almost 3 seconds to load the images.
Then I set up CDN.
I used Cloudflare as the CDN service provider since they offer a free plan.
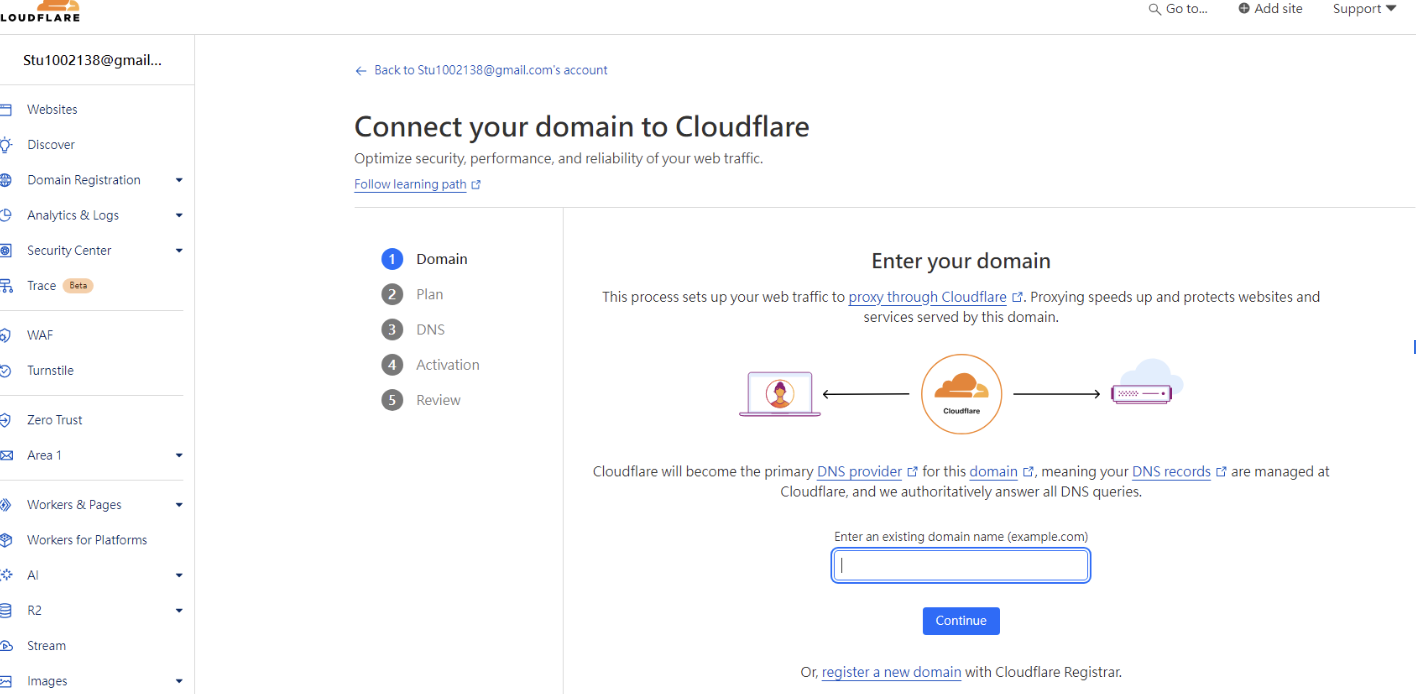
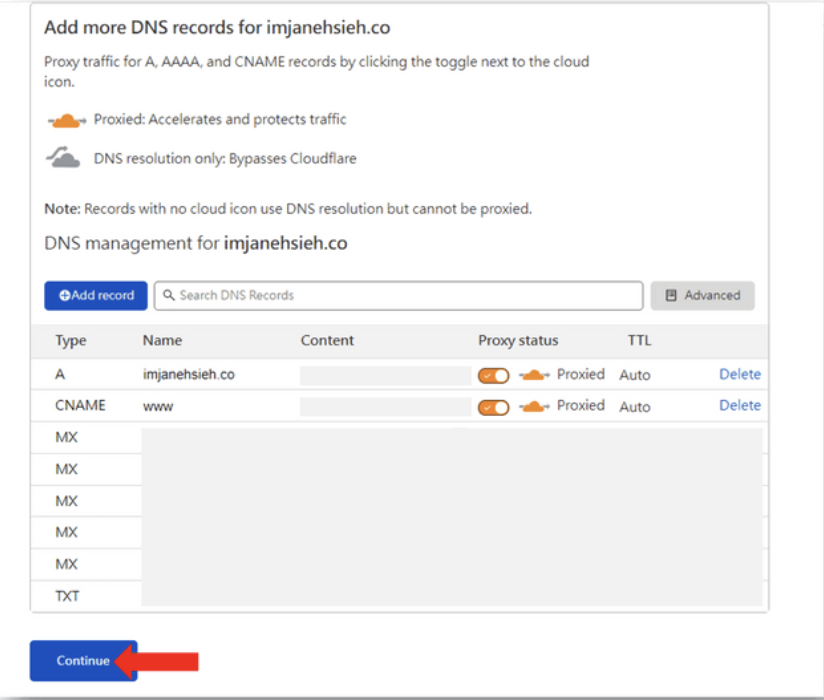
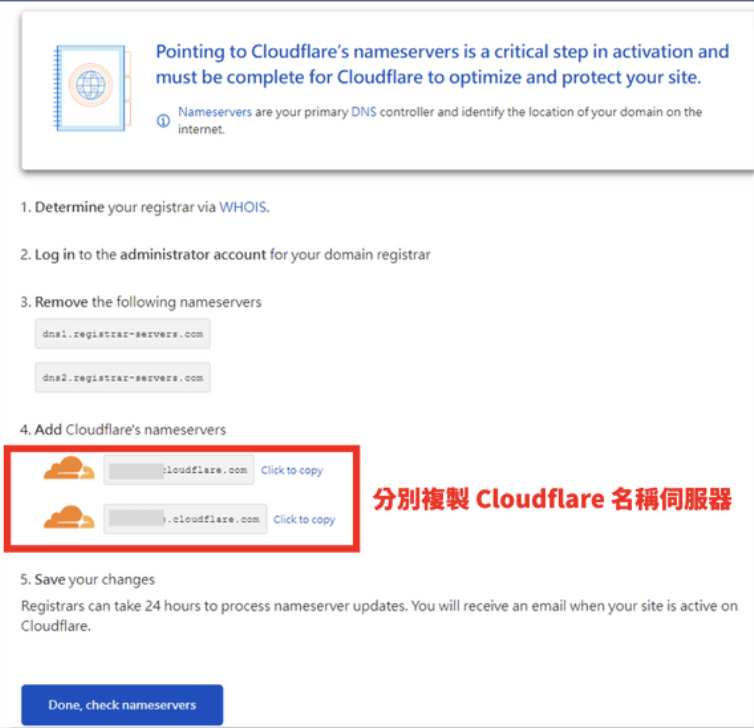
After configuring, there are two main CDN DNS settings required by your domain registrar.
I purchased my domain on Gandi, so I need to configure the domain’s name servers there.
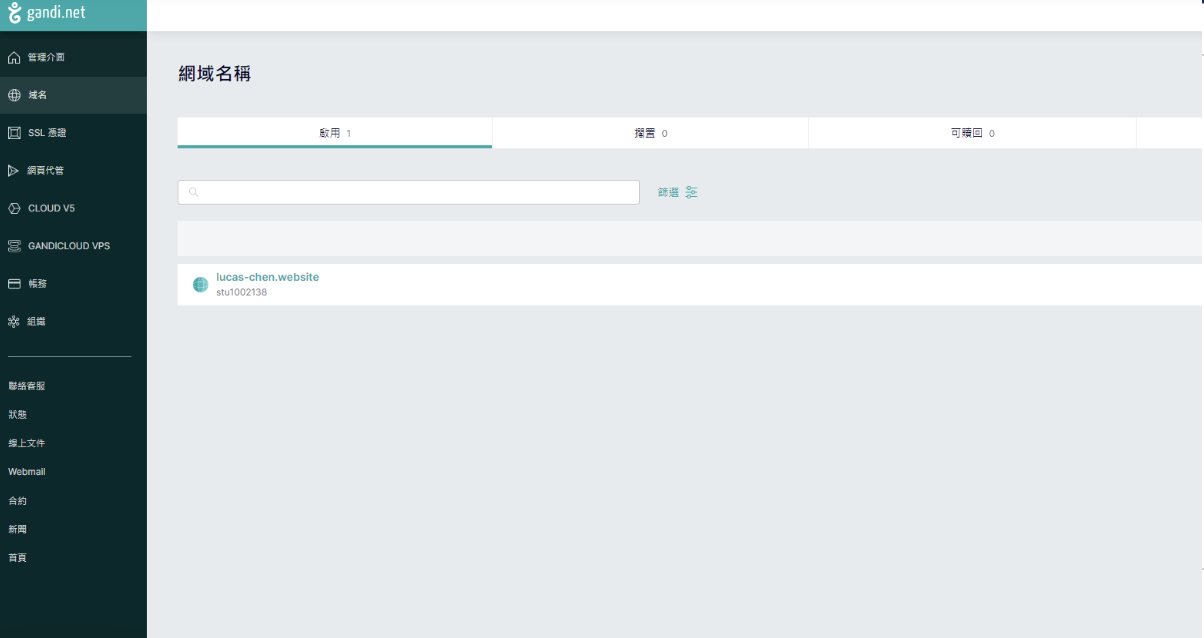
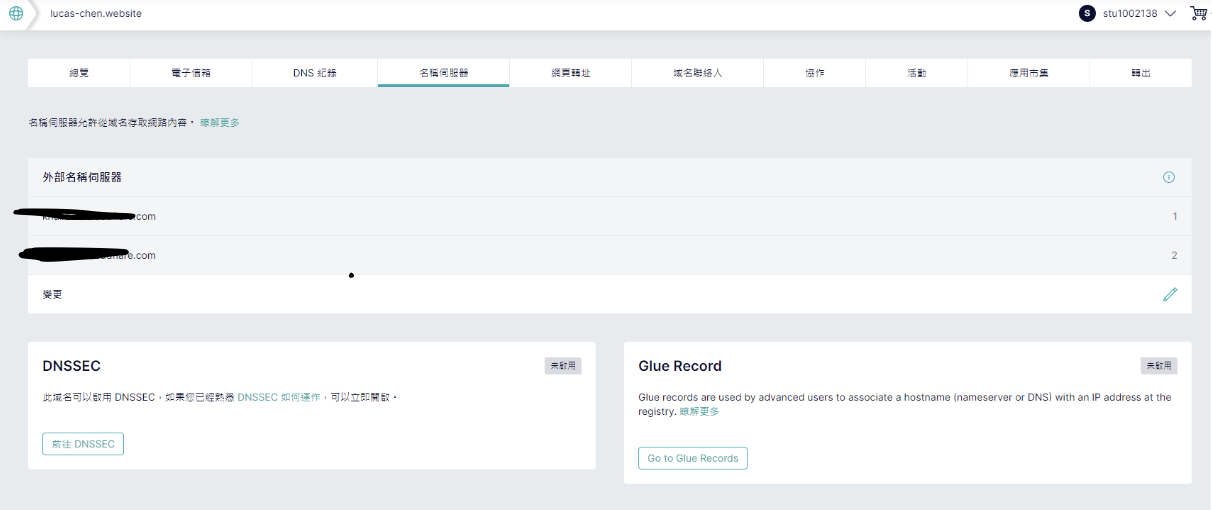
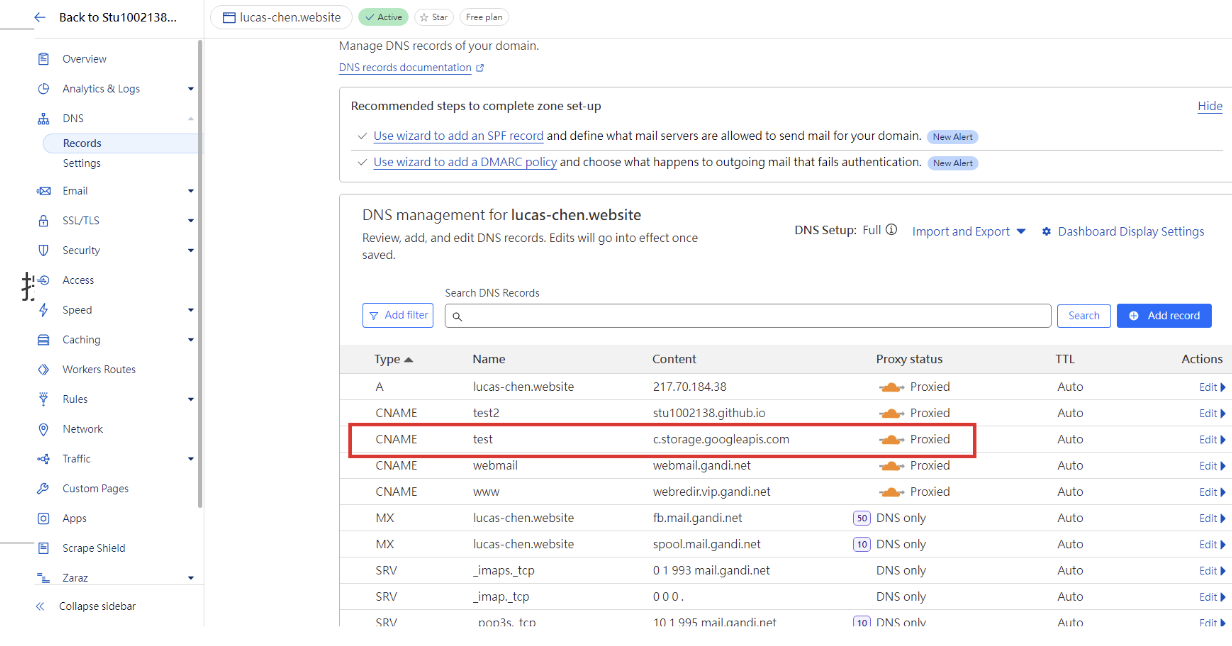
Once configured, it looks like this.
After enabling the CDN, you can observe the significant improvement in loading speed.
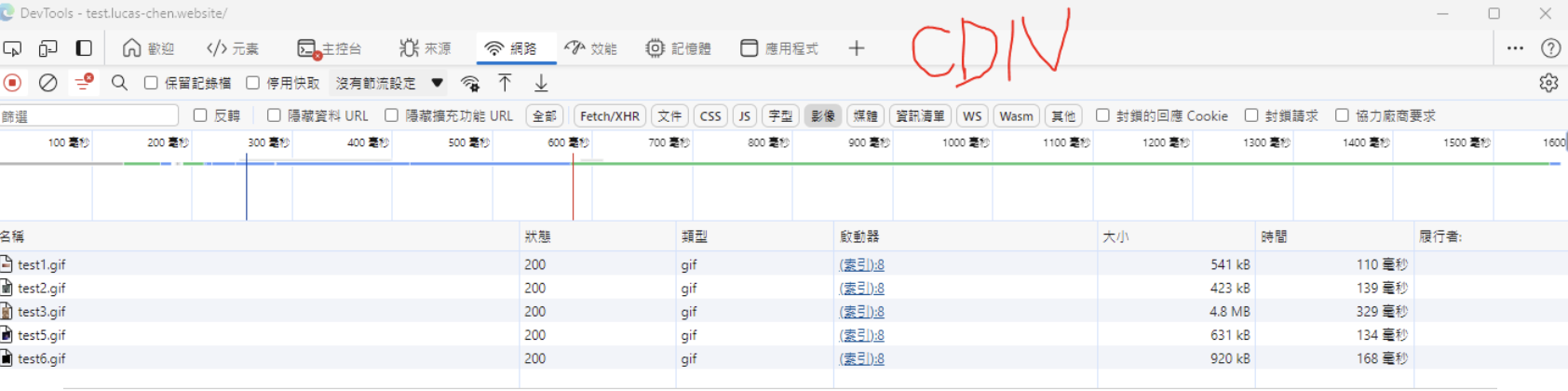
Compared to not using CDN, where each image took almost 3 seconds to load, with CDN, each image now loads in less than 200 milliseconds.
The speed has increased significantly.
How do I check if the website is using CDN?
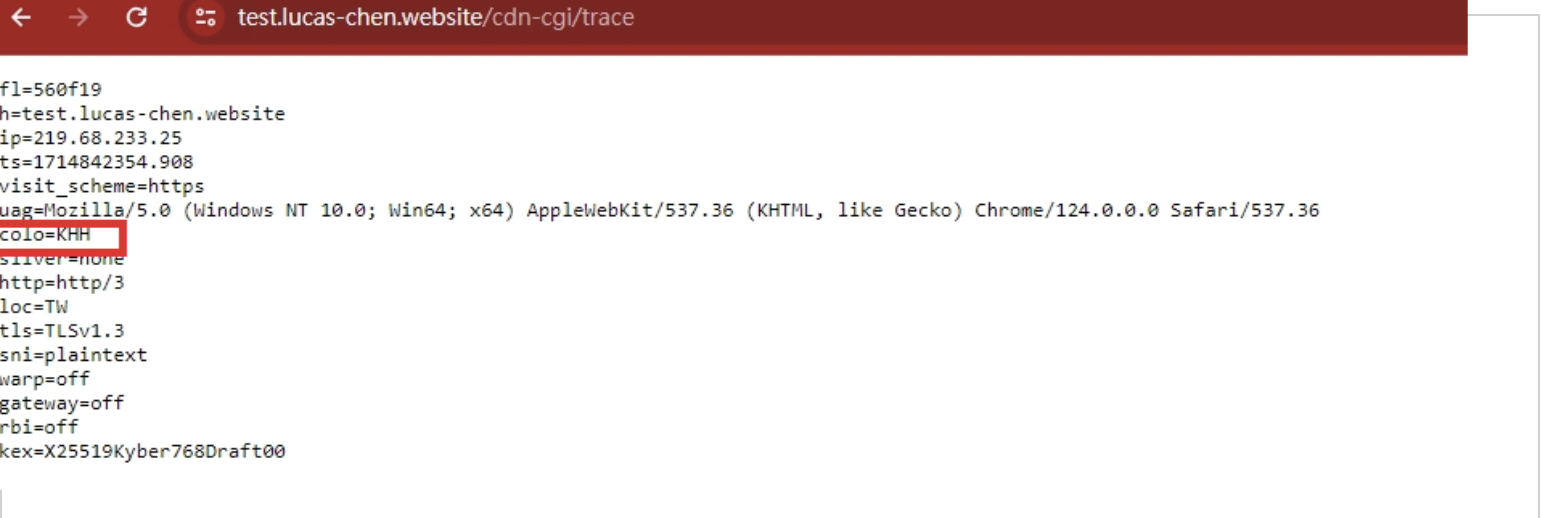
You can add cdn-cgi/trace to the end of the URL.
You’ll see something like colo=KHH, indicating that it’s connected to the Kaohsiung CDN edge server.
For users in Taipei, connecting to Kaohsiung speeds up the connection significantly!
CDN isn’t just for websites; it’s also used for video streaming, software downloads, and game image and video acceleration.
CDN helps improve speed and enhances the user experience.
If there are any parts I missed, feel free to add suggestions.
Thank you all!